sep . 11, 2024 23:27 Back to list
The Discount Effect of Pollination on Pear Trees
The Discount Effect of Pollination on Pear Trees
Pollination is a crucial ecological process that significantly impacts the reproductive success of flowering plants, including pear trees (Pyrus spp.). Pear trees are known for their sweet and juicy fruits, which are enjoyed worldwide. However, their fruit yield and quality are heavily reliant on effective pollination. This article explores the discount effect of pollination on pear trees, highlighting its importance and implications for fruit production.
The discount effect refers to the reduction in fruit yield and quality in the absence of optimal pollination. For pear trees, cross-pollination is often necessary, as many varieties are not self-fertile. This means that for satisfactory fruit set, pollen from different tree species or varieties must be exchanged. Pollinators such as bees and other insects play a vital role in this process. They facilitate the transfer of pollen from the male parts (anthers) of one flower to the female parts (stigma) of another, enabling fertilization and subsequent fruit development.
Without sufficient pollination, pear trees experience a significant discount effect. This can manifest as a decreased number of fruits, smaller fruit size, and lower overall quality. In regions where pollinator populations are declining due to habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change, pear farmers have reported considerable financial losses. Studies indicate that well-pollinated pear trees can yield up to 30% more fruit than those with inadequate pollination, underscoring the economic importance of maintaining healthy pollinator populations.
discount effect of pollination on pear trees
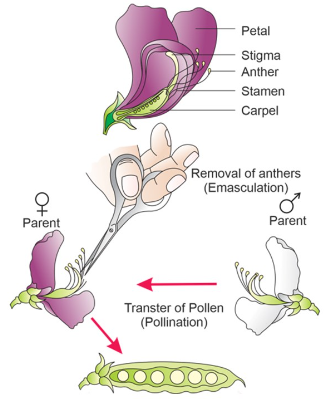
Moreover, the discount effect of pollination on pear trees has ecological implications as well. When fruit yield is compromised, it can disrupt local ecosystems. Birds and other wildlife that rely on pear fruits as a food source may be affected, which can lead to a decline in biodiversity. Additionally, reduced fruit production can impact local economies that depend on pear cultivation, potentially leading to job losses and decreased food availability.
Farmers must take proactive measures to mitigate the discount effect of pollination. This includes planting diverse crops that attract a variety of pollinators, reducing pesticide use, and creating habitats that support pollinator populations. Furthermore, awareness campaigns can educate the public and farmers about the importance of pollinators in fruit production.
In conclusion, the discount effect of pollination on pear trees highlights the intricate relationship between plant reproduction and pollinator health. Effective pollination not only ensures the yield and quality of pear fruits but also sustains ecological balance and economic viability. As we face challenges like declining pollinator populations, it is imperative to prioritize the protection and support of these essential creatures for the sake of our agricultural systems and biodiversity.
-
Precision Artificial Pollination: Maximize Crop Yields
NewsAug.29,2025
-
Premium Plant Pollen: Enhance Yields & Boost Research
NewsAug.28,2025
-
Artificial Pollination: Boost Crop Yields Efficiently
NewsAug.27,2025
-
Premium Kiwipollen for Sale | Male Kiwi Pollen Supply
NewsAug.26,2025
-
High-Quality Apple Tree Pollen for Sale - Boost Your Harvest!
NewsAug.25,2025
-
Pure Plant Pollen: Optimize Pollination & Boost Yields
NewsAug.24,2025