Oct . 12, 2024 17:11 Back to list
best fruit bagging in guava
Best Fruit Bagging Techniques in Guava Cultivation
Guava, scientifically known as Psidium guajava, is a tropical fruit that is not only delicious but also loaded with vitamins and minerals. As the demand for high-quality guavas continues to grow, farmers are seeking innovative techniques to enhance fruit quality and yield. One such technique is fruit bagging, which plays a crucial role in protecting the fruits and ensuring they reach the market in prime condition. This article discusses the best practices and benefits of fruit bagging in guava cultivation.
Importance of Fruit Bagging
Fruit bagging involves placing protective bags over the developing fruits during their growth. This method serves multiple purposes. First and foremost, it shields the fruit from pests and diseases. Guava is susceptible to various insects, including fruit flies, and funguses that can ruin the harvest. By bagging the fruits, farmers can significantly reduce the incidence of pest infestations and minimize the need for chemical pesticides, making their produce more organic and environmentally friendly.
Additionally, bagging protects the fruit from environmental factors such as excessive sunlight, rain, and strong winds, which can cause physical damage or lead to sunburn on the fruit’s surface. As a result, bagging not only improves the aesthetic appeal of the guava but also enhances its flavor and shelf life.
Best Practices for Fruit Bagging
To maximize the benefits of fruit bagging, several best practices should be followed
1. Timing The timing of bagging is critical. Ideally, fruits should be bagged when they are about the size of a marble. This early intervention allows the fruits to develop without the interference of pests and environmental stressors.
best fruit bagging in guava
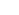
2. Choosing the Right Material The choice of bag material can significantly impact the outcomes. Paper, plastic, or mesh bags can be used, but it is essential to select breathable materials that allow airflow while protecting the fruit from pests. Biodegradable options are preferable for organic farming.
3. Spacing Proper spacing between fruits is important when bagging to ensure that they do not touch each other, as this can promote rot and other diseases. Bags should be sufficiently large to accommodate fruit growth while providing a snug fit.
4. Securing the Bags Bags should be securely fastened to prevent them from being blown away by the wind. Ties or strings can be used, but care should be taken not to damage the fruit in the process.
5. Monitoring Regular monitoring is essential even after bagging. Farmers should check for any signs of pests, diseases, or bag rot. Prompt action can help prevent any potential issues that could affect fruit quality.
6. Removal Bags should be removed as the fruit approaches maturity, typically a few weeks before harvest. This allows the fruit to develop its color and flavor fully.
Conclusion
Fruit bagging in guava cultivation is an effective method to enhance fruit quality and protect against pests and environmental damage. By adopting best practices such as timely bagging, selecting appropriate materials, and monitoring the fruit continuously, farmers can ensure that their guava reaches consumers in optimal condition. As the organic market continues to expand, the importance of such innovative techniques will only grow, ultimately benefiting both producers and consumers alike. The practice of fruit bagging stands out as a prime example of how modern agricultural techniques can harmonize with traditional methods to produce high-quality fruit sustainably.
-
Pollen Peach Tree for Pure Pollination and High-Quality Peach Pollen
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Premium Cherry Pollen for Pure Pollination & Different Types
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for Various Plant Pollen Types
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for All Plant Pollen Types
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Premium Plant Pollen for Pure Pollination & Pollen Block Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for Efficient Crop Yields
NewsJul.28,2025