Nov . 08, 2024 02:43 Back to list
Effects of Environmental Factors on Germination of China Pear Pollen
Understanding China Pear Pollen Germination A Comprehensive Overview
Pollen germination is a critical phase in the reproductive cycle of flowering plants, particularly in the case of the China pear (Pyrus pyrifolia), commonly known as the Asian pear. This process is essential for fruit production, directly influencing crop yields and agricultural practices. The study of pollen germination provides valuable insights into plant reproductive biology and has significant implications for fruit cultivation and breeding programs.
The Importance of China Pear
China pears are increasingly popular due to their crisp texture and sweet flavor, contributing to their rising demand in both domestic and international markets. As a result, understanding the factors that influence successful pollination and subsequent fruit development is vital for farmers and horticulturists. Successful pollen germination is crucial for fertilization, leading to the formation of seeds and, eventually, the development of fruit.
The Pollen Germination Process
Pollen germination begins when compatible pollen grains land on the stigma of a flower. For the China pear, the stigma's surface must have specific characteristics conducive to pollen germination. Once a compatible pollen grain adheres to the stigma, it absorbs water and begins to germinate. This process involves the growth of a pollen tube that penetrates the style and transfers sperm cells to the ovule. The efficiency of this process can significantly affect the fertilization rate and, ultimately, the fruit set.
Environmental Factors Affecting Germination
Several environmental factors influence the germination of China pear pollen
1. Temperature Optimal temperatures are crucial for successful pollen germination. For China pears, studies suggest that temperatures around 20-25°C enhance germination rates. Extreme temperatures, either too high or too low, can adversely affect pollen viability and germination rates.
2. Humidity Adequate humidity levels are essential for pollen hydration and germination. High humidity can support successful pollen adhesion to the stigma, while low humidity may result in pollen desiccation and reduced germination.
china pear pollen germination
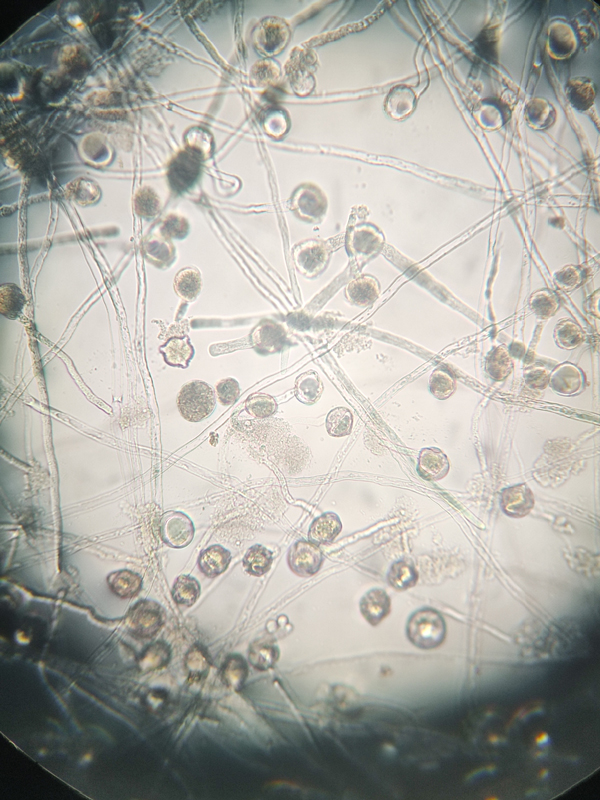
3. Light Conditions While light is not directly necessary for pollen germination, certain light conditions can affect the overall health of the plant and influence flowering timing, thereby indirectly impacting pollen availability and germination success.
4. Soil Nutrients The nutritional status of the soil affects overall plant health, flower development, and pollen viability. Adequate nutrition ensures that the plant can produce high-quality pollen capable of successful germination.
Pollinator Interactions
Pollination is a complex process that often involves various pollinators, including bees and other insects. Effective pollination increases the chances of successful pollen germination. Pollinators not only transfer pollen from one flower to another but also aid in the deposition of pollen on the stigma, creating optimal conditions for germination. The availability of pollinators can vary with seasons and environmental conditions, affecting the reproductive success of China pear trees.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the knowledge gained about pollen germination, challenges remain. Climate change poses a significant threat to the delicate balance of environmental conditions necessary for successful pollen germination. Increased temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and the variability in pollinator populations can drastically influence the reproductive success of China pear.
Future research should focus on developing strategies to enhance pollen viability and germination rates in the face of changing environmental conditions. This could involve breeding programs aimed at selecting for varieties that show improved resilience to environmental stressors.
Conclusion
Pollen germination in the China pear is a vital process that significantly impacts fruit production. Understanding the environmental factors influencing this process, along with the role of pollinators, provides critical insights for horticulturists and farmers. By addressing the challenges posed by climate change and enhancing our knowledge of pollen biology, we can ensure the sustainability and productivity of China pear cultivation, securing its place in both local and global markets. As research continues to evolve, the future of China pear farming looks promising, with the potential for improved varieties and farming practices that bolster fruit yields and quality.
-
Pollen Peach Tree for Pure Pollination and High-Quality Peach Pollen
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Premium Cherry Pollen for Pure Pollination & Different Types
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for Various Plant Pollen Types
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for All Plant Pollen Types
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Premium Plant Pollen for Pure Pollination & Pollen Block Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for Efficient Crop Yields
NewsJul.28,2025