Dec . 06, 2024 22:34 Back to list
pollen for apple trees service
Understanding Pollen and Its Impact on Apple Trees A Comprehensive Overview
Pollination plays a crucial role in the life cycle of apple trees (Malus domestica) and significantly influences fruit production. Ensuring optimal pollination conditions is essential for farmers and horticulturists looking to maximize the yield of their apple crops. In this article, we will delve into the concept of pollen, specifically focusing on its percentage for apple trees, and explore how it affects the growth and productivity of these cherished fruit-bearing plants.
The Role of Pollen in Apple Trees
Pollen is the male gametophyte of seed plants and is vital for reproduction. In apple trees, pollen is produced in the anthers of the flowers during the blooming period. For an apple tree to bear fruit, pollen must be successfully transferred from the male anthers to the female stigma of the same or another apple flower. This process is known as pollination, and it leads to the fertilization of ovules, ultimately resulting in the development of fruit.
Several factors influence the success of pollination wind, insects, and other pollinators. Bees, in particular, play a significant role in pollinating apple trees. Their activities lead to the effective transfer of pollen, which increases the likelihood of successful fertilization. Notably, research indicates that cross-pollination, where pollen from one apple cultivar is transferred to another, often results in better fruit set compared to self-pollination.
Pollen Percentages A Key Indicator
When discussing pollen percentages for apple trees, we generally refer to the ratio of pollen-producing flowers to the total number of flowers on the tree. This metric can indicate the health and vitality of apple tree populations and serve as a forecast for potential fruit yield. A higher pollen percentage usually suggests a greater likelihood of successful pollination, while lower percentages can signal problems that might affect the overall fruit production.
Monitoring and understanding pollen percentages can also inform farmers about the best practices regarding pollination strategies. For instance, if a particular variety of apple tree demonstrates low pollen output, it might be necessary to introduce different varietals nearby to encourage cross-pollination. Choosing compatible varieties can significantly improve pollen transfer efficiency and increase fruit set.
pollen for apple trees service
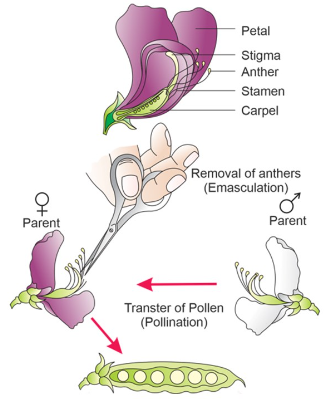
Factors Influencing Pollen Production
Several factors can impact the amount and viability of pollen produced by apple trees. Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, play a significant role in the pollination process. Typically, apple trees bloom in spring when temperatures start to rise. However, unseasonably cold weather can freeze flower buds, leading to poor pollen development and fruit set. Similarly, excessive rain can wash away pollen or hinder pollinators, further reducing the chances of successful pollination.
Other factors include soil health and nutrient availability. Well-nourished apple trees are more likely to produce abundant flowers and sufficient pollen to facilitate optimum pollination. Farmers can enhance soil quality through practices such as crop rotation, composting, and careful fertilization.
The Importance of Pollinator Habitats
Creating and maintaining habitats for pollinators can also positively influence pollen percentages and overall apple production. Planting wildflowers and other nectar-rich plants near apple orchards can attract bees and other beneficial insects, enhancing pollination rates. Furthermore, reducing the use of pesticides can create a more favorable environment for pollinators, ultimately leading to improved fruit yields.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding pollen percentages and their implications for apple trees is essential for effective fruit production. By prioritizing pollination strategies and fostering a conducive environment for pollinators, apple growers can significantly enhance their yield and ensure the health of their orchards. As we continue to learn more about the delicate interplay between pollen, pollinators, and plant health, it becomes increasingly clear that these components work together harmoniously to create the delicious apples enjoyed by many each year. Ultimately, the success of apple cultivation relies not only on the cultivation practices of farmers but also on the understanding of ecological principles guiding pollination.
-
Pollen Peach Tree for Pure Pollination and High-Quality Peach Pollen
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Premium Cherry Pollen for Pure Pollination & Different Types
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for Various Plant Pollen Types
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for All Plant Pollen Types
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Premium Plant Pollen for Pure Pollination & Pollen Block Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for Efficient Crop Yields
NewsJul.28,2025