Jan . 09, 2025 12:38 Back to list
artificial pollination
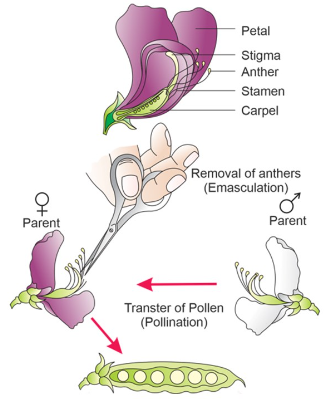
Cross-pollination is a critical biological process that significantly impacts product development, particularly within agriculture and horticulture industries. By transferring pollen from one flower to the stigma of another, cross-pollination fosters genetic diversity, which is paramount for developing resilient plant varieties. This mechanism greatly enhances the adaptability of crops, making it indispensable for agricultural experts seeking to improve plant characteristics such as yield, disease resistance, and environmental stress tolerance.
Authoritativeness in this field is also reflected in the literature and research studies conducted by botany and genetics specialists. Scientific publications provide evidence-based insights into how cross-pollination influences plant evolution and adaptation. Industry professionals, equipped with this authoritative knowledge, can make informed decisions to maximize crop performance and quality. The findings outline the long-term benefits of maintaining genetic diversity within plant populations, underscoring the importance of cross-pollination in sustaining agricultural ecosystems. Trustworthiness is achieved through transparent and consistent efforts in research and application. A reliable cross-pollination program is built upon a foundation of data-driven approaches and verified methodologies. Collaboration between scientists, farmers, and industry stakeholders enhances trust by sharing information on best practices and innovations. Successful case studies from reputable agricultural firms serve as proof of concept, showcasing the tangible advantages of implementing well-orchestrated cross-pollination strategies. As we delve deeper into an era characterized by climate unpredictability and increased agricultural demands, the function of cross-pollination becomes even more pertinent. It is not merely a natural occurrence but a pivotal tool in crafting future-fit crop varieties. By embracing the principles of experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness, industry leaders can effectively utilize cross-pollination to address challenges related to crop productivity and resilience. The ongoing commitment to research and application in this domain promises to uphold cross-pollination as a cornerstone for future advancements in agriculture and product development.

Authoritativeness in this field is also reflected in the literature and research studies conducted by botany and genetics specialists. Scientific publications provide evidence-based insights into how cross-pollination influences plant evolution and adaptation. Industry professionals, equipped with this authoritative knowledge, can make informed decisions to maximize crop performance and quality. The findings outline the long-term benefits of maintaining genetic diversity within plant populations, underscoring the importance of cross-pollination in sustaining agricultural ecosystems. Trustworthiness is achieved through transparent and consistent efforts in research and application. A reliable cross-pollination program is built upon a foundation of data-driven approaches and verified methodologies. Collaboration between scientists, farmers, and industry stakeholders enhances trust by sharing information on best practices and innovations. Successful case studies from reputable agricultural firms serve as proof of concept, showcasing the tangible advantages of implementing well-orchestrated cross-pollination strategies. As we delve deeper into an era characterized by climate unpredictability and increased agricultural demands, the function of cross-pollination becomes even more pertinent. It is not merely a natural occurrence but a pivotal tool in crafting future-fit crop varieties. By embracing the principles of experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness, industry leaders can effectively utilize cross-pollination to address challenges related to crop productivity and resilience. The ongoing commitment to research and application in this domain promises to uphold cross-pollination as a cornerstone for future advancements in agriculture and product development.
Next:
Latest news
-
Pollen Peach Tree AI Management with GPT-4-Turbo
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Eco Fruit Paper Bags for Peak Freshness | Durability Focused
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Pollen Peach Tree for Pure Pollination and High-Quality Peach Pollen
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Premium Cherry Pollen for Pure Pollination & Different Types
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for Various Plant Pollen Types
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Artificial Pollination Solutions for All Plant Pollen Types
NewsJul.29,2025